What is unpasteurized ("raw") milk?
Unpasteurized milk—sometimes called "raw" milk—is milk that has not been treated to remove harmful germs through pasteurization. When milk is pasteurized, it is heated to a temperature at which harmful germs are killed.
Pasteurization is an important step in getting milk safely from the farm to your table. Germs found in the environment can contaminate milk at any point in the production process. Most commonly, germs that get into milk come from animal feces (poop). Even on the cleanest farms, poop particles are present:
-

On and around the animals' udders
(the part of a cow, goat, or other animal that produces milk)
-
In the environment (including in soil, water, or animal poop/manure)
-
On the equipment used to milk an animal
When someone drinks raw milk, they also are drinking any germs that may be in the raw milk. These germs can make a person sick. These disease-causing germs can also be found in milk products such as cheese and creams that are made from raw milk. Eating or drinking unpasteurized milk products can also make people sick.
What are the health risks of eating or drinking something made with raw milk?
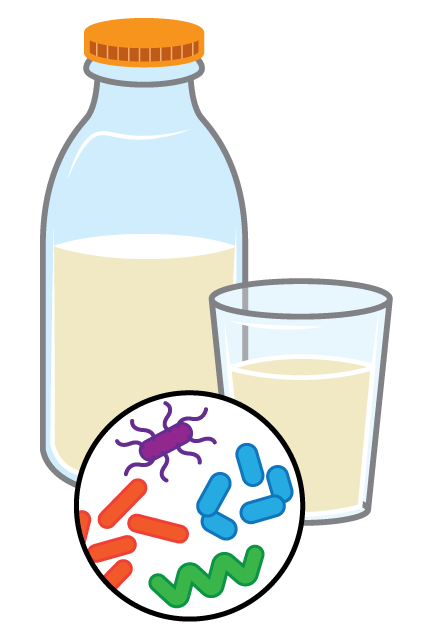

Raw milk and dairy products made from raw milk can contain harmful bacteria such as:
Although not as common, raw milk can also contain germs such as
Brucella,
Cryptosporidium,
Mycobacterium bovis, and
Yersinia. Many of these germs naturally live in the intestines of farm animals.
Germs from raw milk can make people sick. The bacteria most commonly found in raw milk can cause symptoms such as:
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
- Vomiting
- Fever
Other conditions such as muscle weakness and paralysis (from
Campylobacter), sudden kidney failure and anemia (from
E. coli O157:H7), or miscarriage in pregnant women (from
Listeria monocytogenes) can also occur.
Isn't raw milk supposed to be healthy?
There is no difference in the nutritional value between raw milk and pasteurized milk. Raw (unpasteurized) milk is not the same as organic milk or milk that comes from grass-fed animals, and it does not mean it is better for you than pasteurized milk. Raw milk can still contain harmful bacteria even if it is organic, from grass-fed animals, or from very clean farms.
Raw milk also cannot give you "good bacteria" (also called
probiotics). Probiotics can be found in pasteurized dairy products such as yogurt or kefir, which are safer to eat than raw milk.
For more questions and answers about raw milk, please see the
U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Raw Milk Questions and Answers webpage.
Are raw milk and raw milk products available in California?
Raw milk from cows, sheep, and goats may be legally sold in California if a dairy farm meets specific requirements for sanitation and licensing. Animals at the facilities and farms that are approved to sell raw milk in California must be tested for specific diseases, including brucellosis and tuberculosis. Farm workers at these facilities must also be free from infectious germs and pathogens that can contaminate milk and make people sick.
There is no guarantee that these measures will produce raw milk dairy products that are free from harmful germs or are as safe to eat or drink as pasteurized milk products. That is why farms that produce and sell raw milk must include a warning label on all raw milk dairy products which tells people that the product they are purchasing may contain bacteria and germs that can make them sick. In fact, although these precautions and legal requirements are in place, contamination of raw milk still occurs, and there have been recent recalls of raw milk products and disease outbreaks in California.