Healthy Weight for Healthy Birth and Beyond

Why a healthy weight in pregnancy matters
Weight before and during pregnancy affects the health of pregnant individuals* and their babies.
Pregnant Individuals
Individuals who are overweight or obese before pregnancy or gain excessive weight during pregnancy have increased risk for numerous adverse health conditions such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, cesarean delivery and hypertension.1,2 In 2002-2007, obesity contributed to about one-quarter of pregnancy-related deaths.3 Among individuals who died of pregnancy-related causes, nearly twice as many were obese as compared with all who gave birth in California (32% vs. 17%).3 In addition, obesity was a risk factor for hospital readmission following birth.4 Excessive weight gain during pregnancy is associated with macrosomia, a condition in which an infant is large for its gestational age. This may result in delivery complications and lead to a caesarean delivery.5 Excessive weight gain during pregnancy is also correlated with postpartum weight retention, which can lead to a higher risk of gestational diabetes and other adverse health outcomes in future pregnancies.2
Infants
Infants born to individuals that are obese are less likely to be breastfed and are at an increased risk of being diagnosed with attention deficit disorder, autism or developmental delays, and depression or anxiety.6,7 Infants born to individuals that are overweight or obese have a higher chance of being overweight or obese in childhood.8 Childhood obesity can lead to cumulative health problems such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, high cholesterol, asthma and sleep apnea.9

Overweight & obesity before pregnancy:
A growing problem in California
In 2018, more than half (53%) of individuals were overweight or obese prior to pregnancy.10 The average pre-pregnancy height and weight among individuals ages 20 and over with a live birth was 5’4” and 155 pounds which corresponds to a Body Mass Index (BMI*) of 26 (overweight). Normal weight for this height is 108-145 lbs. based on a BMI of 18.5-24.9.
(BMI = weight [kg]/height [m2])
The maps in Figure 1 show the increase in the percent of individuals who entered pregnancy overweight or obese by county from 2009 to 2018. As reflected in the maps, p who are overweight or obese has increased from 46% in 2009 to 53% in 2018. In 2009, just under half the counties had rates of 50% or higher of overweight or obese pregnant individuals, but no counties with rates greater than 60%. By 2018, three-fourths of the counties had rates of 50% or higher of overweight or obese pregnant individuals with 15 counties over 60%. The Central Valley Region has the highest rate of overweight or obese pregnant individuals.
Race/Ethnicity
In California, excessive pre-pregnancy weight differs by race and ethnicity (Figure 2). Three in four (77%) Pacific Islander individuals enter pregnancy overweight or obese, followed by Hispanic, American Indian and Black individuals with approximately three in five (65%, 64% and 61% respectively) entering pregnancy overweight or obese. Less than half (43%) of White individuals enter pregnancy overweight or obese and less than one in three (30%) Asian individuals enter pregnancy overweight or obese.10
*BMI may overestimate or underestimate body fatness in some individuals since it does not take into consideration an individual’s muscle or bone mass. The clinical correlation of BMI has not been validated in some subpopulations, therefore BMI should not be used as the sole criteria for making health recommendations.
“In California, excessive pre-pregnancy weight differs by race and ethnicity.”
Figure 1: Individuals Who Were Overweight or Obese Prior to Pregnancy, 2009 and 2018
11
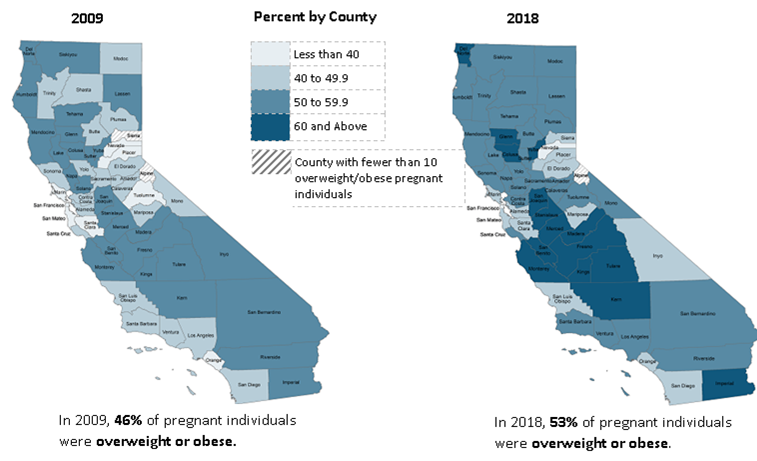
In 2009, 46% of pregnant individuals were overweight or obese
In 2018, 53% of pregnant individuals were overweight or obese.
Figure 2: Percentage of Individuals with a Recent Live Birth Who Were Overweight or Obese Prior to Pregnancy by Race/Ethnicity, CA, 2018 10

Figure 3: Percentage of Individuals with a Recent Live Birth Who Were Overweight or Obese Prior to Pregnancy by Delivery Payer, CA, 2018
10

Insurance Type
Individuals who had Medi-Cal coverage (California's Medicaid program) for labor and delivery were more likely to enter pregnancy either overweight or obese (61%), compared to those with non-Medi-Cal insurance coverage (47%) (Figure 3).
10
Excess weight gain in pregnancy: another problem
Recommended Pregnancy Weight Gain Guidelines The National Academy of Medicine, previously the Institute of Medicine (IOM), provides guidelines on recommended weight gain during pregnancy that are specific to an individual’s BMI prior to pregnancy.1 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) developed weight gain guidelines for pregnant individuals bearing twins.5 Following these weight gain guidelines can reduce the risk of adverse health outcomes during and after pregnancy.1
Underweight (BMI<18.5)
|
28-40 lbs.
|
N/A
|
Normal Weight (18.5-24.9)
|
25-35 lbs.
|
37-54 lbs.
|
Overweight (BMI 25.0-29.9)
|
15-25 lbs
|
31-50 lbs
|
Obese (BMI > 30.0)
|
11-20 lbs.
|
25-42 lbs.
|
Weight Gain During Pregnancy by Pre-Pregnancy Weight Status
During pregnancy, about three in 10 (35%) individuals gain the recommended amount of weight based on their pre-pregnancy weight status (Figure 4). Approximately two in 10 (24%) pregnant individuals gain too little and about four in 10 (42%) gain excessive weight. Notably, more than half of those who are overweight/obese prior to pregnancy gain an excessive amount of weight.10 Gaining an inappropriate amount of weight during pregnancy increases the risk of the occurrence of adverse health outcomes for the individuals and the infant.
Figure 4: Weight Gain During Pregnancy by Pre-Pregnancy Weight Status (BMI), 2018
10
Evidence Based Intervention
Health care providers monitor and promote healthy weight status prior to pregnancy and appropriate weight gain during pregnancy using multicomponent diet and physical exercise counseling.
1,12
References
- Rasmussen KM, Yaktine AL, Institute of Medicine (US) and National Research Council (US) Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines, eds. Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2009. doi: 10.17226/12584
- Thunell L, Davis KE. Nutrition Counseling and Healthy Weight Gain During Pregnancy: A Systematic Review. Women's Health a dietetic practicegroup of the Academyof Nutritionand Dietetics. 2019;(2):1-7.
- The California Department of Public Health. Pregnancy-Associated Mortality Review.Report from 2002-2007 Maternal Death Reviews. Sacramento, California: Department of Public Health, Maternal, Child and Adolescent Health Division; 2018 https://www.cdph.ca.gov/ Programs/CFH/DMCAH/CDPH%20Document%20Library/ Communications/Profile-PAMR.pdf
- Clapp,M.A., Little,S.E., Zheng, J. et al. The relative effects of patient and hospitalfactorson postpartum readmissions. JPerinatol. 2018; 38, 804– 812. doi:10.1038/s41372-018-0125-8.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Weight Gain During Pregnancy. CDC. pregnancy-weight-gain.htm. Updated January 17, 2019. Accessed August 25, 2020.
- Jo, H., Schieve, L. A., Sharma, A. J., Hinkle, S. N., Li, R., & Lind, J. N. Maternal prepregnancy body mass index and child psychosocial development at 6 years of age. Pediatrics. 2015;135 (5):e1198-e1209. doi:10.1542/peds.2014-3058.
- Bever Babendure, J., Reifsnider, E., Mendias, E., Moramarco, M. W., & Davila, Y. R. Reduced breastfeeding rates among obese mothers: a review of contributing factors, clinical considerations and future directions. International Breastfeeding Journal. (2015);10, 21. doi:10.1186/s13006-015-0046-5.
- Voerman, E., Santos, S., Patro Golab, B., Amiano, P., Ballester, F., Barros, H., Jaddoe, V. W. V. Maternal body mass index, gestational weight gain, and the risk of overweight andobesity across childhood: An individualparticipant data meta-analysis.PLoS Med. (2019);16 (2), e1002744. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002744
- CDC. Childhood Obesity Causes & Consequences.CDC.cdc.gov. https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/childhood/causes.html. Updated June 11, 2020. Accessed August 25, 2020.
- Data Source: California Comprehensive Master Birth File, 2018. Percentages may not total 100 due to rounding.
- Data Source: Birth Statistical Master File, 2009 and California Comprehensive Master Birth File, 2018.
- Amorim AR, Linne YM, Lourenco PM. Diet or exercise, or both, for weightreductioninwomen after childbirth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;(3):CD005627. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005627.pub2.